Let’s start with a question that might sting a little…When did we all become so bad at thinking and focus solely on being panicked?
AI industry in panic after China’s DeepSeek overtakes ChatGPT and Meta— The Independent
or
Chinese AI threat triggers $1 trillion market crash— The Telegraph
or
DeepSeek tech wipeout erases more than $1 trillion in market cap as AI panic grips Wall Street— Business Insider
Have you had enough of these?
People sell/act first, think later (or never).
Algorithms amplify fear, headlines scream about China’s AI leap, and everyone’s left scrambling to separate reality from runaway hype.
Here’s how one shockwave enhances the next:
Initial Shock: DeepSeek R1's launch on January 20 shocked the tech community with this bold and provoking comparison between R1 vs. OpenAI o1.
It started on Reddit, X ... on January 23. Then, news outlets quickly picked up the headlines on January 25, and every content creator spread fear and uncertainty.
Finally, when the market opens… traders and investors start selling off tech stocks. Nvidia sank 17% in one day on Monday, nearly 600B in market value.
High-frequency trading algorithms detect the sudden surge in sell orders and automatically initiate more sell orders, creating a cascading effect.
As stock prices plummet, more investors are compelled to sell to avoid further losses, creating a self-sustaining cycle of panic selling.
It is much easier to hit “sell” or repost how DeepSeek makes Sam Altman panic than to ask, Wait—what exactly are we panicked about?
This isn’t about dismissing concerns.
I simply refuse to drown in the noise.
As always, my article won’t spoon-feed you with my conclusion. Instead, I will walk you through my thought process while interrogating you with guided questions in clear categorization. You get to pick what is most critical to you.
Very simple, three parts:
We’ll start with everything you need to know about the epicenter (Who?).
The technology and cost (How and Why is DeepSeek R1 different from OpenAI o1?).
Map the shockwaves (With critical questions on each aspect).
Finally, a Survival Toolkit that sums up the red flags to spot via a mindmap template for you to download and expand your own thoughts at your own pace.
Epicenter, High-Flyer Capital, DeepSeek, Liang Wenfeng.
It began in a Shanghai high-rise in 2021.
Liang Wenfeng, was a hedge fund manager who made a billion-dollar bet that would alter AI history.
As his team at High-Flyer Capital developed trading algorithms, Liang quietly ordered staff to acquire every available Nvidia A100 GPU in Asia. It is estimated he hoarded 10,000 chips through shell companies for faster stock predictions. At least, that was the plan in 2021.
Then, in 2022, the Biden administration restricted the export of advanced computing chips.
The Pivot
2023, Chinese regulators cracking down on quant funds. Liang stunned investors by redirecting 90% of their assets into an AI startup. Skeptics walked out; true believers stayed to build DeepSeek.
Trial by Fire
Rumor says… the early prototypes leaked in 2024 through a junior engineer's GitHub account. But of course, this stays as a rumor. What we do know, DeepSeek has polished open-source models that undercut rivals. Here’s their Github.
Breakthrough
The rise of DeepSeek has been nothing short of a disruptive underdog story. Think of it as “Temu of AI.”
In May 2024, DeepSeek shook up the industry by releasing DeepSeek V2 as an open-source model, sparking a full-scale price war… at least in China.
On December 26, 2024, they did it again. With DeepSeek V3, the prices are even lower, redefining industry expectations: $0.14 per million tokens.
Shock and Awe
On January 20, 2025, R1 was released. The news on everyone’s feed— R1 architecture delivers OpenAI o1 level reasoning at 1/10th the compute cost. By Monday, January 27, 2025, triggers a $1T tech stock selloff (17% drop in Nvidia + 5.6% sector-wide decline) as investors question Nvidia's AI infrastructure dominance.
Technology
A basic understanding of why DeepSeek R1 is so special is the foundation for you and me to ask critical questions.
Three most important technical breakthroughs from DeepSeek’s R1 model. With no-brainer analogies, don’t worry, even if you aren’t a techie. Here’s the R1 Paper (only if you are interested, of course).
The "Teamwork" AI Design (Mixture of Experts— MoE)
Instead of a "jack-of-all-trades" AI like OpenAI o1, think of R1 as a team of specialized experts collaborating like a kitchen crew.
There’s a master chef (the teacher model) who then trains line cooks (small models) through knowledge distillation. So a powerful AI can run on your laptop while staying smart, like getting Michelin-star meals from your home kitchen at a low cost.
MoE focuses on modularity and specialization for efficient task handling; OpenAI o1 emphasizes deep reasoning within a single model framework optimized for complex problem-solving.
Self-Taught Reasoning (using only Reinforcement Learning)
DeepSeek’s AI learned to reason on its own by trial and error, without extra guidance. It was given problems (math, coding) and rewarded for correct answers and logical steps.
Think of teaching a kid to ride a bike or play puzzle by letting them figure it out and rewarding the kid if they’ve done well. In contrast, OpenAI o1 is more like providing a structured problem-solving method and refining and improving within that framework.
Predicting Multiple Steps Ahead (Multi-Token Prediction)
The old way is like a chess player who only thinks one move ahead. On the other hand, DeepSeek R1 is like a chess player thinking several moves ahead.
DeepSeek R1 predicts several words or steps at once. In comparison, OpenAI's o1 prioritizes deeper reasoning with step-by-step problem-solving.
Knowledge Condensing (Distillation)
Imagine you’re preparing for an exam. You have the option to go with a 1,000-page textbook or a 100-page study guide that captures the key points, summaries, and essential concepts.
While the study guide doesn’t include every detail from the textbook, it’s compact and efficient enough to help you perform well on the exam.
In AI terms, the textbook is the large, complex AI model (the "teacher"). The smaller, distilled model (the "student") is the study guide. The process of creating the study guide is knowledge distillation.
Key questions you should ask to separate DeepSeek reality from hype:
Is DeepSeek making AI smarter or just cheaper? DeepSeek’s model performance is on par with U.S. models in reasoning tasks, but did it surpass the existing models?
How easy is it to distill a model into one that’s cheaper to train and run? If it is easy enough, where’s the advantage of releasing a larger, more advanced one that’s much more costly to run?
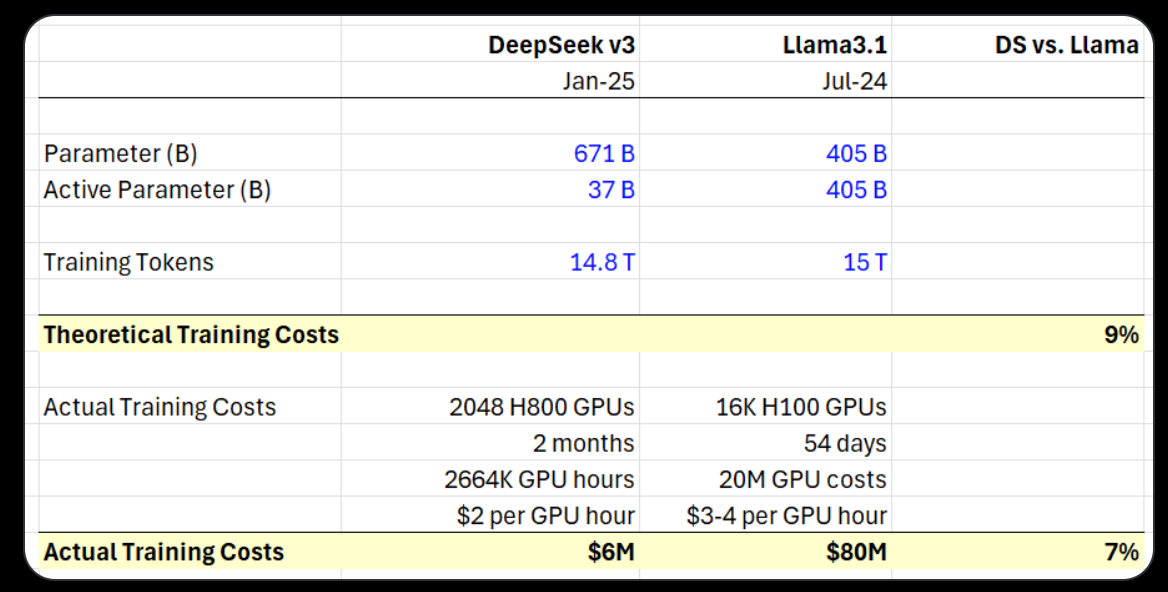
Training Cost
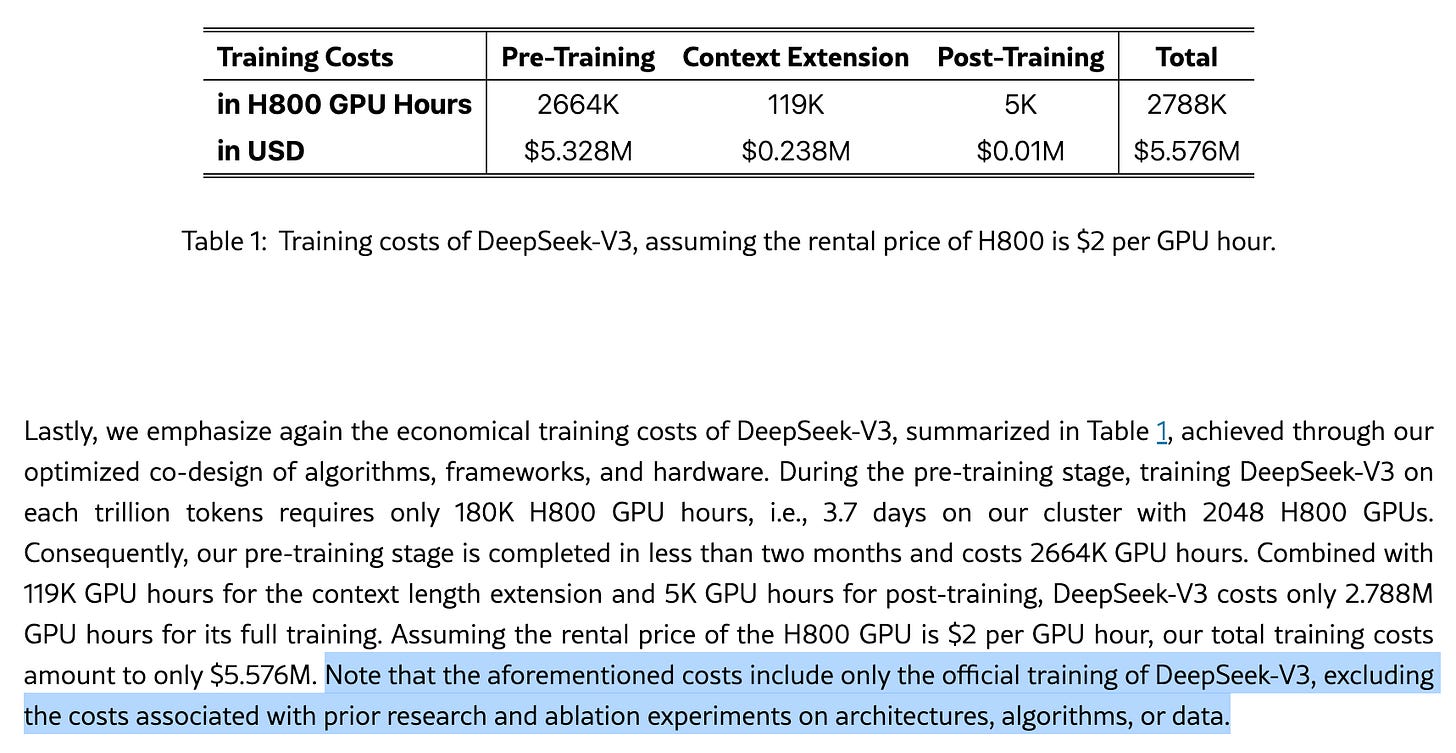
DeepSeek's claim of ultra-low training costs for their AI model has raised eyebrows in the tech community.
It is also evident in their report that the training cost has excluded costs associated with prior research, ablation experiments on architectures, algorithms, or data.
Still, the million as the unit of training cost starkly contrasts with the billions spent by US tech giants. If true (the H800 and the hours), it will disrupt the established business models. The precise methodologies underlying DeepSeek's breakthrough remain undisclosed.
There’s also a back-of-envelope calculation from an analyst that supports the low-cost claim.
Those who question the claim:
Some data scientists questioned that DeepSeek was developed with only 2,000 chips. They noted that the company might have operations with tens of thousands of Nvidia chips that could have been used in development.
Don't worry if you don't get any of these.
A main takeaway is, aside from the report by DeepSeek, no one yet can confirm their claim about training costs. It can be true… but we don't know until someone can replicate a similar model with an equally low cost.
Key questions for you to ask:
What’s the catch of this low cost? Could there be a tradeoffs, e.g., What can’t this AI do well, and why?
Now, you’ve learned the foundation.
Mapping the Shockwaves
Shockwave #1: Major Tech Players.
DeepSeek R1 and more threaten the core premise of existing AI giants: dominance requires scale (more data, more compute, more $$).
If a lean Chinese startup can match OpenAI o1’s reasoning at 1/10th the cost, what does that mean for the "spend billions to win" playbook?
Would Microsoft, Google, and Meta spin up their version of R1? or maybe the question is when instead of if? Or has their investment need just enormously gone down once they figure R1 out?
What would OpenAI do to survive against a high-performance, open-source rival?
How defendable are the existing big AI companies against small(er) companies that act nimble like DeepSeek?
What’s more valuable? AI models or training data? If it’s data, who owns the largest consumer data source, or the most unique dataset?
Shockwave #2: Chip Industry & Infracture.
Many news and influencers argue that Jevons Paradox will kick in. Simply put: Cheaper models → More startups (more AI usage) → More GPU buyers.
But what factors must exist for the Jevon paradox to be true? To say the least, it requires elastic AI demand, market needs, and other complementary resources to be available (e.g., engineers know how to build an efficient model as R1 does).
So questions you should ask:
Will cheaper AI models create a positive feedback loop of higher demands in AI usage?
Could Nvidia face more competition, and do smaller GPU makers stand a chance?
Is the current model’s problem with hallucinations a dealbreaker?
Would the $100B (or $500B as Trump announced) project Stargate become stranded assets if leaner AI dominates… or does it mean more capacity or just less investment needed?
Will AI eventually become a commodity, as I predicted?
Shockwave #3: Copyright Infringement and Data Privacy.
DeepSeek’s success raises tricky legal and ethical questions about who truly “owns” AI, the data, or the model used to train the next generation.
At the center of the debate is distillation (where a large model “teaches” a smaller model) and the copyrighted content used to train the earlier LLMs. Since the massive dataset is the fuel, where do privacy and intellectual property rights fit?
Questions to ask
Is distillation a form of copyright infringement? How does distillation differ from traditional learning methods?
A follow up, if distillation a form of copyright infringement, what about all the content used by companies like OpenAI when training their model?
If yes, who owes what, and how much is owed, and to whom?
If, at some point onwards, all we use is AI-generated content to train, who will compensate the original content creator or data owners? And how do we get new content that isn’t in the training set yet?
How should data privacy concerns be addressed in AI training?
Good read: OpenAI’s privacy policy. The first sentence in the policy:
When you visit, use, or interact with the Services, we receive the following information about your visit, use, or interactions…
DeepSeek’s policy, collects certain information when users set up an account).
It’s really about who you want to give your data to…The Chinese government or American commercial companies.
Shockwave #4: Startups & Smaller AI Firms
Yes, lower-cost training and inference could open doors for resource-strapped ventures. But does that also mean smaller players suddenly face a more crowded space, competing with DeepSeek itself and a throng of new entrants?
Does R1 inspire/empower more companies to build their AI, or does it drive competition to a fever pitch?
Would there be a flood of “DeepSeek-inspired” founders lead to a market glut?
If VC sees a cheaper path to AI breakthroughs, do they ask their investees to pivot away from existing AI ideas to chase these leaner models?
If inference is cheaper to run, does that lead to higher adoption and application in new domains? Are we going to see even more AI embedded in other products if the cost of operating it drops?
Shockwave #5: Enterprises & End Users
DeepSeek isn’t pushing AI to do anything dramatically “new” regarding raw capabilities. It’s distilling knowledge from existing large models at a fraction of the usual cost. Would This efficiency revolution trickle down to enterprises and end users?
DeepSeek’s super low pricing has surely put pressure on giants, how might this change who can afford AI services?
To the enterprises, if AI’s training cost is now a fraction of what was predicted, what’s the next costly but finite resource to fight for? Host? or Talent?
Instead of a technical leap forward in intelligence by DeepSeek it is rather a cost revolution. However, that economic shift alone can significantly change how enterprises plan, deploy, and pay for AI. And how quickly people see tangible benefits every day.
Shockwave #6: Geopolitical & Regulatory
DeepSeek’s apparent success amid export controls spotlights a broader power struggle. Can bans on high-end chips (like Nvidia’s H100) actually curb AI development? Western nations face a choice: double down on regulations or adapt to a new competitive reality.
Does hardware scarcity lead to more software ingenuity (like DeepSeek’s approach), or is the breakthrough inevitable just a matter of time?
Are export controls working against US interests in the long run?
Does Stargate project risk squandering funds on brute-force computing while China invests in leaner, more advanced techniques?
Like engineers rushed into Silicon Valley, are we about to see a wave of global talent shifting to Chinese startups and away from FAANG?
How would Trump respond to fast-tracked visas for AI talent?
Could the EU capitalize on the low-cost model? Or does Europe’s slower-moving bureaucracy keep it at a disadvantage?
The Near-Term Future? and Download the DeepSeek Hype Survival Toolkit.
While others are still panicking about DeepSeek's efficiency breakthrough, the smart ones ask more profound questions about where this leads us.
What about the near-term future?
The Real AGI Question R1-Zero's self-training capabilities raise fascinating possibilities. But instead of asking, "Is this AGI?" ask:
What happens when AI can self-learn and self-improve at a fraction of today's cost?
The real opportunity in DeepSeek's breakthrough isn't just about cheaper AI. It's about who can ask the right questions and act accordingly.
Here’s the mindmap for you: Survival Toolkit.













Share this post